











InstElectric - Electricity

وصف لـInstElectric - Electricity
Tool to support the calculation of electrical installations that will allow the user (designer / electrician / technician) to perform electrical calculations easily and quickly.
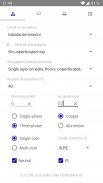
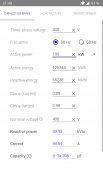
· Dimensioning complete of low voltage circuits with the most frequent installation methods
· Phase cable size, neutral, protective conductor
· Criteria based on the admissible current of the cable, voltage drop and overcurrent protection
· Designation of the most used cables.
· Circuits with automatic circuit breaker until In = 4000 A (Ir rating setting), maximum fuse In = 1600 A (gG type), maximum 12 conductors parallel per phase, maximum size 630 mm²
· Estimate of the maximum short-circuit current (simplified method)
· Forecast of loads of a building destined to houses with several sections: dwellings, common services, commercial premises/offices and garage with/without infrastructure for recharging electric vehicles
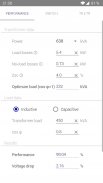
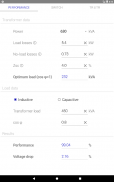
· Reactive power of the capacitor bank for the compensation of the power factor (cos φ) and capacity (µF) of the capacitors
· C/K Factor for automatic capacitor bank
· Choice of installation system in the function of the circuit, cable and its situation
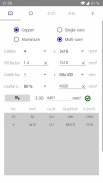
· Power in an unbalanced three-phase system
· Overvoltages due to loss of neutral conductor, earth fault and short circuit
· Electricity parameters of a single-phase or three-phase (balanced)
· Transformer performance
· Secondary voltage of a transformer acoording to switch position
· Size of trays and conduits
· Conduits characteristics according to the installation method
· Conversions of wire sizes (mm²-awg) and conduits threads
Parameter settings for calculations:
· Constants (voltages, conductivity, temperatures, etc.) that affect electrical calculations
· Protections (circuit breakers and fuses)
· Selection of minimum rate for circuit-breakers with regulation and maximum cable size for multi-conductor grouping per phase
· Method estimation of the reactance
· Conductivity of the conductor depending on the current of the circuit (constant, according to the expected current, maximum cable temperature)
· Use reduction factors by grouping cables/circuits
· Use of factors of diversity/utilization
· Reference documents: IEC Standards, REBT (sp), Technical Application Guide, (UE) 2016/364
IN NO CASE SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT OR INDIRECT DAMAGES AS A RESULT OF THE CORRECT OR INCORRECT USE OF THE APPLICATION
أداة لدعم حساب التركيبات الكهربائية التي ستتيح للمستخدم (مصمم / كهربائي / فني) إجراء الحسابات الكهربائية بسهولة وبسرعة.
· أبعاد كاملة من دوائر الجهد المنخفض مع أساليب التثبيت الأكثر شيوعا
· حجم الكابل المرحلة ، موصل محايد ، واقية
· معايير تستند إلى التيار المقبول للكابل ، وانخفاض الجهد وحماية التيار الزائد
تعيين أكثر الكابلات استخداما.
· دوائر مع قاطع دارة أوتوماتيكي حتى في = 4000 A (إعداد تصنيف الأشعة تحت الحمراء) ، أقصى فتيل في = 1600 A (نوع gG) ، أقصى 12 موصل بالتوازي لكل مرحلة ، الحد الأقصى لحجم 630 مم²
· تقدير الحد الأقصى للتيار ماس كهربائى (طريقة مبسطة)
· توقعات الأحمال من مبنى مخصص للمنازل التي تحتوي على عدة أقسام: المساكن والخدمات العامة والمباني التجارية / المكاتب والمرآب مع / بدون بنية أساسية لإعادة شحن السيارات الكهربائية
· القوة التفاعلية لبنك المكثف لتعويض معامل القدرة (cos φ) والسعة (µF) للمكثفات
C / K عامل للبنك مكثف التلقائي
· اختيار نظام التثبيت في وظيفة الدائرة والكابل ووضعه
السلطة في نظام ثلاثي الأطوار غير متوازن
· الجهد الزائد بسبب فقدان موصل محايد ، خطأ الأرض وقصيرة الدائرة
· معلمات الكهرباء لمرحلة واحدة أو ثلاث مراحل (متوازنة)
أداء المحولات
الجهد الثانوي للمحول acoording للتبديل الموقف
حجم الصواني والقنوات
خصائص القنوات وفقا لطريقة التثبيت
تحويلات أحجام الأسلاك (مم² - awg) وقنوات الخيوط
إعدادات المعلمات للحسابات:
· الثوابت (الفولتية ، الموصلية ، درجات الحرارة ، إلخ) التي تؤثر على الحسابات الكهربائية
· الحماية (قواطع الدوائر والصمامات)
اختيار الحد الأدنى لمعدل قواطع الدائرة مع التنظيم والحد الأقصى لحجم الكابل لتجميع متعدد الموصلات في كل مرحلة
طريقة تقدير التفاعل
· الموصلية اعتمادا على تيار الدائرة (ثابت ، وفقا للتيار المتوقع ، أقصى درجة حرارة الكابل)
· استخدم عوامل الاختزال من خلال تجميع الكابلات / الدوائر
· استخدام عوامل التنوع / الاستخدام
الوثائق المرجعية: معايير IEC ، REBT (sp) ، دليل التطبيقات التقنية ، (UE) 2016/364
في أي حال من الأحوال ، يكون المؤلف مسؤولاً عن أي أضرار مباشرة أو غير مباشرة كنتيجة لاستخدام التطبيق الصحيح أو غير الصحيح





















